Cisco Extension Mobility
In the Communications Manager Solution we have the ability for users to possibly move around the environment. In a centralized deployment we could have people go from the corporate office maybe to a branch location. Now I’m thinking they’re not going to tote their phone with them but it sure would be nice when they got to the destination if they could log into an IP Phone and have their user specific configuration such as their directory number, their privileges, even voicemail access. That’s what we can do with Extension Mobility. They could log into the phone, pull in the background screen and the directory number, and all the information just like you would use roaming profiles on a computer solution, you could use the same concept with Extension Mobility. It’s implemented as a service, so you have to subscribe to this service and we can use this within or across clusters. So it doesn’t just have to be centralized. I think of it primarily in a centralized environment, but you could have multiple clusters that you’re using and that also could leverage Extension Mobility.
Cisco Extension Mobility Login Process
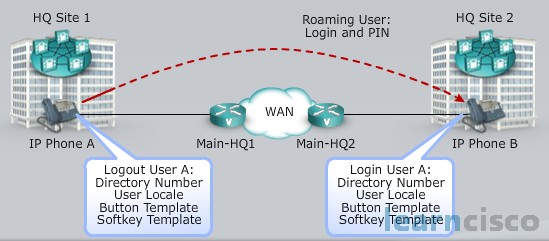
Now let’s say we have that user that’s moved and they’ve gone from the corporate location to maybe a branch location. What they’ll do is they’ll press the service button on an IP phone. This is going to allow them to log in. So they’ll have to put in an authentication user ID and PIN to gain access to this. And after we’ve been authenticated it’ll select the device profile that’s been associated with this user. If we had multiple profiles which we’ll talk about, the user will be prompted for which one they want to choose. And then the IP phone configuration is updated with these new parameters. Now it resets and it loads the updated configuration for that individual user. Now there maybe some issues in the fact that I moved from like headquarters to branch location, think about my PSTN access, my privileges. They may need to be adjusted for where I’m located within the network. So we’ll look at that as well, but before that here is the list with the steps explained above:
- User presses the services button on an IP phone and selects the Cisco Extension Mobility service.
- The user is authenticated by User ID and PIN.
- After successful authentication, Cisco Extension Mobility selects the device profile associated withthe user (prompts user to select if multiple associations exist).
- The IP phone configuration is uploaded with the configuration parameters from the device profile.
- The IP phone resets and loads the updated configuration.
Cisco Extension Mobility Default Device Profile
As an administrator we need to go in and assign the Extension Mobility service to phones that users are going to log in to. Now think about this, you might have conference rooms or maybe some offices where people that come to visit could go in and log in to those phones. We want to make sure though that we have a device profile that includes the appropriate information when nobody’s logged in. In other words I don’t want the phone to not be active, I want it to be usable to make phone calls so we have this device profile. It’s not really associated with a physical phone but it has all the properties of a device except like the MAC address and maybe directory information. And when we’ve loaded this into the device, the device adopts those attributes of that device profile. So if a user logs in to the phone then they get their specific settings. The user device profile will replace the existing configuration of that device for them and when they log out the log out profile will replace that device profile. So again, we want to make sure that first of all users could log in to any type of phone, whether or not they’re associated with that particular phone model or not and then second of all we want to make sure that the device that people are using to log in to has some type of profile associated with it, so we can use it as an IP phone.
Intercom
We have the ability to setup an intercom line and here the user can call the intercom line obviously of another user which autoanswers the call, but it’s doing it using one-way audio. Why? Well I don’t think it’d be a good idea if you could call into somebody’s office with the door closed and they are having a financial discussion and you could eavesdrop.

So that’s the purpose. You have to call in, they have to recognize. They hear “oh, it’s Michele. Can you pick up?” and now the recipient can initiate the two-way conversation. And I think it’s great for security reasons. We don’t want to just open up the path and be able to eavesdrop. So we have what we call audio whispering capabilities with our intercom solution.
Intercom with Connected Line State
Let’s say you’re on the phone, and your assistant needs to contact you. Now let’s say they initiate the intercom connection. So I’m in an active call, the voice of the active caller and the intercom lines are mixed. So I hear you in my ear. Now I can chose to accept that call or I can ignore it and not accept it. So we have the ability, even with a connected line state, to understand that somebody needs to talk to you urgently maybe, and receive that information and either A initiate that two-way conversation on the intercom or B – not initiate that two-way conversation, let it go. Person will probably hang up, you know, you can kind of setup the parameters that you want to and we can maintain that active call.
Intercom Architecture
Now how do we configure our intercoms? Well, there’s an option to setup a speed dial. So with the speed dial the intercom line is preconfigured. If we don’t have pre-configuration with a speed dial then we have to dial the number that we’re trying to reach. And they have their own permissions. Here’s another thing too, you may want to control who can intercom with each other. So we have calling search spaces that get created and they contain the configured partition of the party that we’re able to call and vice versa. So for a number of target intercom lines the configuration of calling search spaces needs to be verified. In example we have an assistant helping a couple of managers. We would need to make sure that they have permissions to establish this intercom communication again through partitions and calling search spaces.
Our Recommended Premium CCNA Training Resources
These are the best CCNA training resources online:
Click Here to get the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp, the most comprehensive and highest rated CCNA course online with a 4.8 star rating from over 30,000 public reviews. I recommend this as your primary study source to learn all the topics on the exam.

Want to take your practice tests to the next level? AlphaPreps purpose-built Cisco test engine has the largest question bank, adaptive questions, and advanced reporting which tells you exactly when you are ready to pass the real exam. Click here for your free trial.
